 |
| Green Building Diffusion |
Water (like heat) always flows from areas of higher
concentration to areas of lower concentration. If there is moist, wet
soil on one side of a foundation wall, it will try to find a way through
the concrete foundation wall and into the dry, warm basement. It is
very important to correctly waterproof foundations and install footing
drains to move moisture away from the building. Damaged to
foundation is
difficult and expensive to repair, and can cause a whole host of other
house problems. Capillary Action
Water can be sucked or pulled through many
building materials. It can actually travel uphill and cause unseen rot
under siding or under shingles. Builders have to think like water and
carefully seal the smallest of gaps in a structure. Proper flashing and
detailing is key to help prevent this problem.
Airflow
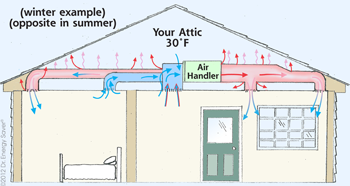 |
| Green Building Airflow |
If
air can get into a wall cavity, so can moisture. As building occupants,
our daily activities such as showering, cooking and even breathing
create a lot of moisture. A plastic vapor barrier applied to the studs
under the drywall helps prevent mold from growing in the wall. It is
important to put a system in place to catch this moisture and
controlling its movement.
Good quality exhaust fans and making sure that
the dryer vent is correctly installed are both important steps. Better
yet, eliminate the cavity, or the space between the studs, that holds
insulation that allows air flow. Spray cellulose or spray urethane foam
do this job well.
See Also:
Comments
Post a Comment